|
"Traumatic events are extraordinary, not because they occur rarely, but rather because they overwhelm the ordinary human adaptations to life."
- Judith Herman, Trauma and Recovery When you hear the word, "trauma," what comes to mind? Growing up, I placed trauma in a category of things I only heard about on the news. Events like plane crashes, robbery at gunpoint, or natural disasters made sense to me. Of course they were big and terrible and traumatic--the news said so! However, as I got older, I realized that there was much more grey area about what was actually considered trauma or not. Some trauma is publicized, but other times thoughts about it can become so difficult that even one's closest friends do not know about it. Furthermore, trauma to one person may not be considered trauma to another. In these cases, is it still considered trauma? While some trauma can take a very clear and pervasive form, like in the cases I mentioned above, it can also be more subtle and even happen over a period of time. Often, individuals do not seek out the counseling treatment they need because they do not feel like their experiences were "bad enough." If you are wondering if you have experienced trauma and should consider counseling, I recommend asking yourself two questions. First, do you have experiences in your life that you would define as traumatic? I'm not asking whether your aunt or the newspaper or your Facebook feed calls it traumatic. Instead, I want to know how YOU feel about your experiences. If you have experienced an event in your life that you define as traumatic and want to talk about it, I would urge you to consider calling a counselor. You may be surprised by how healing it is to have your story of trauma validated by an objective individual. Perhaps you are certain you have experienced trauma, but still do not know if you should consider counseling. In that case, my second question to you is this: are you having difficulties in life that you did not have before the trauma occurred? For example, you may find that you struggle to sleep through the night, have an increased/decreased appetite, or have difficulty completing tasks efficiently at work or school. Or maybe the experience of the trauma has become so pervasive that you can't seem to stop thinking about it. By seeing a counselor, you can begin to develop coping skills that will reduce your post-traumatic symptoms and help you feel more functional in your daily life. If you can answer yes to one or both of these questions, it may be time to consider reaching out for trauma therapy. Healing is possible when you are willing to commit the time to properly honor your story in the context of a safe relationship. Written by Christian Swan on March 09, 2017
1 Comment
Practicing this DBT Skill can help us stay grounded and connected this holiday season! Mindfulness is a skill that, when practiced regularly, is a great tool to reduce stress, connect with our personal goals and create genuine connection with others. The holidays can be rich in memory, sentiment and relationship. They can also be full of family expectations, grief and reminders of trauma. These, and many more experiences, can overwhelm, cause us to disregard our own needs, and flood us with many different emotions. In order to enjoy the positive aspects of the holiday and skillfully navigate the challenges, try practicing mindfulness throughout your holiday season!
Mindfulness has three components:
Mindfulness as Stress-Reduction For many, the holiday season means a busy schedule and many more tasks and to-dos than normal. Practicing mindfulness in the midst of the whirlwind helps to produce moments of calm to catch our breath and remember our priorities. Mindfulness also helps us evaluate where our time and energy are going and make the most intentional decisions for ourselves in this season. Mindfulness as Social Support Paying attention to the present moment, without judgement can give us a lot of important information about what is happening in a room, or in a conversation. In the midst of a holiday gathering, take a moment to simply observe what is happening inside and outside of yourself. Allow yourself the gift of a few deeper breaths. Notice who is talking with who, and what those dynamics are like. Notice what is happening inside yourself as you connect with different people. Hold this information lightly and without judgement, and allow this information to guide your interactions. Mindfulness to support Intentional Decisions If you find yourself navigating a lot of spoken and/or unspoken expectations over the holidays, mindfulness skills can help you identify your needs and desires and to stay connected to them throughout the season. Spend some intentional moments noticing where you would like your time and energy to go this season, what would make it memorable and special for you and yours. Notice how other’s expectations are making you feel, especially if those expectations cause you to disregard your own needs and desires. Give yourself the gift of staying connected to yourself and your values, which becomes a much more congruent and grounded holiday experience. Have you lost a loved one and find yourself in a never-ending sea of grief? The process of mourning typically takes much longer than we anticipate. As a grief therapist, I know that grief can take a long time, often extending years after a significant loss. There is no protocol for how long grieving is meant to take. In fact, the grief process is wholly informed by the relationship itself. However, there may be some reasons that we may extend the grieving. If this is your experience, you may be encouraged to know that moving through grief emotions and adjustments may help you remember more from your time with your person.
1. We hang on to grief as a way to stay close to our person Grief and mourning are an intense and all-consuming experience. When we are processing and feeling and adjusting on such an intense scale, our brain is much less available for it’s normal functions. It is common to feel brain fog while grieving. The griever may be tempted to stay in this phase of grief because it centers the person that they lost. The focus is on the relationship and the stories are about the person. The pain seems to point back to their person. The logic here is that staying in the pain of grief must be the only way to stay connected to the person who is now gone. There is a time for all grievers when the pain eases, the emotions have softened and the adjustments are starting to feel normal. It is important to acknowledge when the grief seems to be letting up. And the good news here is that when the griever is out of “survival mode,” they are able to access many more memories and stories from their time with their person. There is a sense of gaining more of them back as the grief softens. 2. We hang on to grief because we don’t know what comes next Another common experience for those grieving a significant loss is a fear and confusion about the future. Moving forward in life without your person seems impossible for so many reasons. As uncomfortable as the grief experience can be, it does become familiar terrain after a while. For some, the temptation is to stay in the grief because it is familiar instead of navigating the uncertainty of the future. Considering a new future is a creative task, and one that is unwelcome at first. Our imaginations fail to offer a vision of what our lives might offer us as we move forward. Even so, it is important to choose to allow yourself a new future. Moving toward the opportunities that open ahead of you does not mean that you leave your person in the past. In fact, your forward motion can be propelled by the strengths you have gained through your experiences with your person. We may be able to use their memory as a spring-board toward what comes next, imagining them as an encouraging and empowering voice nudging us forward. It is a lovely thing to learn to carry our person with us as we continue in life. Only the griever will know if they are hanging on to their grief unnecessarily. It is an internal milestone, marked by choice in the depths of a grief-stricken heart. If you find yourself wondering if it might be time to move forward and feeling stuck in your grief, please reach out for some support. Our team is available to help navigate all phases of this process! When we are grieving, we often ask ourselves, “when will I start to feel better?” Seasons of grief are intense and demanding in ways that we don’t experience otherwise. The emotional burden is great, our relationships may be strained as the result of our grief, and everything feels so far from normal. It is natural and normal to long for the end of these feelings. So, what does it look like to engage our grief in a way that leads to healing?
1. Learn to Tolerate and Accept the Difficult Emotions Grief requires us to befriend the most uncomfortable emotions. Grief emotions—shock, sadness, confusion, anger, longing, disorientation, despair—are all terribly uncomfortable to feel. And when our loss is significant, we end up feeling them for much longer than we ever expect. We increase our grief suffering when we fight against the grief emotions—ignoring, avoiding, overcompensating, engaging addiction—these all end up heightening our emotional experience. Additionally, when we don’t tend to our emotions, they may come out sideways in ways we don’t intend. We can help our grief process along by looking at each grief emotion that we find ourselves feeling and explore its source, its history, its message. In doing so, we are almost listening to the emotion, giving it time and space to breathe. For some, these grief emotions signal danger or threat. Take the time to disentangle these historical messages and learn to welcome each emotional character. In time each of the grief emotions will soften. 2. Notice and Name all of the Adjustments The other major focus of grief work is making many (sometimes hundreds!) of life adjustments. Without our person in our life, we may find ourselves needing to learn new skills, take on new tasks, fill new roles. Each one of these adjustments can take an enormous amount of emotional energy, during a time in life when energy is at a minimum. It is important to be aware of these adjustments, to bring them into focus by noticing and naming them. Even better, to be talking with an understanding person about them. Sometimes, we can slow the pace and take just one or two tasks or activities at a time. Other times, we just need to keep moving forward and taking care of business. Regardless, naming the many adjustments can be very helpful in processing grief and moving forward in healing. Notice for yourself how difficult these tasks feel. How are you navigating them today? Does your support system know you are working and healing in these ways? What can you request your people do for you as you engage grief healing? If you are in need of a skilled and sensitive grief therapist, please reach out to our team! We understand these tasks and are available to help create safety and opportunity for doing this work! Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) offers a set of skills to help with many different emotional and relational difficulties. The four pillars of DBT are Mindfulness, Emotion Regulation, Interpersonal Effectiveness and Distress Tolerance. Each of these pillars offers a number of skills to practice in that area. I have selected three DBT skills that I believe can make a significant difference for those managing depression.
Depression is an experience that includes a slow-down or freeze response in the nervous system. People managing depression may feel numb, detached, hopeless and sad. These internal experiences may cause them to isolate from relationships, get stuck in their difficult emotions, struggle to complete normal activities. Often, those managing depression feel misunderstood by the people in their life, especially when they are encouraged to “think positively” and “just get over it.” In fact, people managing depression are often expending enormous effort to engage in their life in the most simple ways. The following set of DBT skills can be used together or individually to improve depression symptoms and help catalyze healing and forward movement. 1.Emotion Regulation Skill: Opposite Action When we are using Emotional Regulation skills, we are paying attention to whether or not our emotions fit the situation we are in. Opposite Action is a skill that we reach for when we have determined that our emotions DO NOT fit the facts of the situation. This is often the case with depression. Depression is like a lens that makes life look harder and sadder than it actually is. All emotions have an action urge, an instinctual action that the emotion makes us want to do. When our emotions DO NOT fit the situation, we benefit from acting opposite to the action urge. Here are some common emotions experienced in depression and suggestions for opposite action.
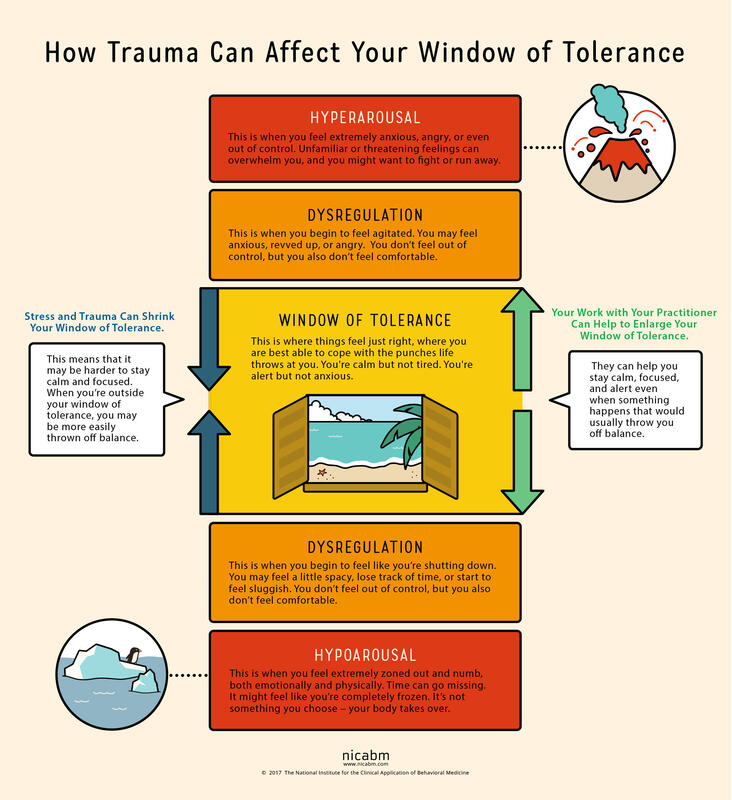
2.Interpersonal Effectiveness Skill: Making Requests Making Requests is a relationship skill that is very closely related to making boundaries. Requests highlight what we need from another person. While they can be vulnerable to make, they are also vital to communicating our needs with others. Loved ones are not mind-readers and need invitations and instructions to know how to care for those managing depression. People experiencing depression are almost always misunderstood by the people who care for them most. Unless they have experienced depression themselves, loved ones will likely minimize the depressed experience. From the outside, it may appear that it would only take a few simple steps to recover from depression. If only that were true. In order to stay connected with loved ones and to receive the care they absolutely need, those managing depression need to lean into this skill of making requests. They need to speak about how they are feeling and the effort they are expending to engage with their lives. They need to ask their loved ones to be patient with them, to use encouraging language, to offer comfort and presence rather than solutions. 3.Distress Tolerance Skill: Radical Acceptance We reach for distress tolerance skills when we are going through circumstances that are too big and/or too hard for us to change. Depression often comes on the tails of a big and hard life event, such as the loss of a loved one, a difficult transition, a painful event or unmovable circumstances. When there is truly nothing we can do to change our circumstances, we need to shift our focus toward acceptance. We are using radical acceptance skills when we work to create openness and willingness toward our difficult circumstances. Willingness is a powerful mindset shift and means that we will stop fighting against what is inevitable. Endlessly fighting against unfavorable circumstances is a recipe for suffering. Pain is inevitable in our lives, but suffering is a choice. We can still live meaningful lives in the midst of painful circumstances. When we give up the fight, we are more able to find acceptance. . . and peace. Living with depression can be a completely consuming experience. Those experiencing depression can have symptoms like persistent sadness, hopelessness, lethargy, low self-esteem, guilt, worthlessness, and more. These symptoms exist on a spectrum from mild to severe and short to long-term. Living day to day with depression feels heavy, aimless and dark. Often people suffering from depression are told to change their mindset in order to recover. We know that change must come from a much deeper place. In fact, living day to day with depression requires enormous amounts of courage and perseverance, and it helps those who are suffering to have this acknowledged and validated. Depression has several different causes and sources. There are strong inherited patterns for major depression. There are also significant hormonal impacts, especially in post-partum depression and pre-menstrual depressive disorder. Personality also has a strong influence on mood and energy and motivation. All of these different also create causes can also produce a predisposed sensitivity to depression. This blog post is to highlight when life circumstances or traumas are the source of depression. When this is the case, it is the nervous system that is leading the body and mind toward depression. And as such, treatment will need to be focused on healing the nervous system and helping the client work toward a different nervous system state. When the nervous system (read: trauma, overwhelm, life circumstances) is causing depression, healing must happen deeply in the autonomic (involuntary) nervous system. To understand the nervous system impact and the healing of nerves, we need to understand the Window of Tolerance. When we are in the window of tolerance, we are grounded, flexible and able to roll with the ups and downs of life. When we have a good amount of resilience, our window of tolerance is large and we are able to handle significant challenges without becoming too dysregulated. When we are under a lot of stress, our window of tolerance shrinks and we start to experience hyper or hypo arousal. Let’s discuss these nervous system states that exist outside of the window of tolerance. When we experience overwhelming stressors, we become dysregulated in one of two different directions, sometimes cycling between the two. We can become activated and have a flood of anxious or angry energy wash through our body (hyperaroused). Or we can become deactivated and experience numbness and a shut down response (hypoarousal). This hypoaroused state is the embodiment of depression. This is how stressors or traumas cause depression.
Hypoarousal symptoms also exist on a spectrum. On the milder side, we might experience tiredness, brain fog and a slump in energy. When hypoarousal is heightened, one might experience emotional numbness, dissociation, and even catatonia. Sometimes, we end up in this depressed state after an extended period of stress. It’s like our system is saying that it can’t handle that level of activation for that long and it shuts down. In other words, depression can be caused by a nervous system shut down. So, what does our nervous system need when it is in this shut down state? Sometimes, it simply needs a break. It needs rest from the hyper-activated state. The nerve that runs these activation pathways has become raw and overworked and needs to be soothed. The nervous system also has a significant need for connection when it is in this state of shut down. It needs a form of connection that is accepting, supportive and understanding. The nervous system also needs a way to process or integrate the overwhelming emotions that shut it down in the first place. This typically needs to happen at a slow and measured pace, so not to overwhelm again. These interventions serve as a ladder that helps us climb out of the shut down state, closer and closer to that window of tolerance. For a sustained healing process, we also need to take a good look at our lifestyle. When healing from a nervous system shut down, we need to choose a gentle pace of life, avoiding any additional stressors when possible. We can boost our nervous system health with meditation and mindfulness skills. We can invest in sustainable sleep habits that allow our entire system to regenerate every night. Gentle, joyful movement practices can also lift us out of shut down or depression. We at Benediction honor your nervous system and it’s inherent needs and functions, and we know how to move you out of harmful nervous system pathways. We can help you reconnect with yourself and with others by bringing your system back into balance in that lovely window of tolerance. Losing someone we love is always a heartbreaking and emotionally difficult experience. Grief is the word we use to describe the set of emotions we have and the emotional process we experience related to that important loss. Grief can feel gentle and straightforward or it can feel extremely difficult and consuming, or any variety of this. Grief is often a very natural process of healing from a loss. Sometimes, though, we can get stuck in the healing process and need support to move forward. It might be helpful to understand the different circumstances that might cause us to get stuck.
Grief is often a completely confusing, disorienting, painful and lonely experience. There are many elements of our modern society and culture that make this experience that much more difficult and lonely. Bereavement, grief and mourning are very natural and necessary experiences, and they have the potential to be traumatic and/or transformative. One of the greatest gifts the bereaved can receive is the presence of a compassionate companion. Let’s take a closer look at what it means to offer this meaningful and healing companionship to someone who is grieving.
The most effective way to mourn after a loss is to share your thoughts and feelings (grief) with a compassionate listener (grief companion). The Grief Companion HOLDS SPACE for those who are grieving by providing a safe and empathetic presence in which the mourner can begin to explore the terrain of their inner world. HOLDING SPACE for the mourner is your contribution to their care. The grief companion does not guide the mourner, instead allows the mourner to choose the path. True expertise of grief lies with (and only with) the unique person who is grieving. More specifically, Grief Companionship is being present to another person’s pain. The Grief Companion is willing to go into the wilderness of the soul with the bereaved. This is a spiritual journey, not only an intellectual journey. The Grief Companion is committed to bear witness to the struggles of the bereaved without judgement, direction, or quick fixes. They allow the disorder and confusion that so often afflicts the bereaved. They trust that the bereaved will find their way through the jungle of emotion and joins their journey with compassionate curiosity. Central to the role of Grief Companion is the art of honoring stories. In telling the story of their love and loss, mourners:
The art of Grief Companionship involves slowing down, becoming acquainted with the mourner’s inner world, and to really listen as the mourner embraces the reality of their loss, their pain, important memories and search for meaning. Each of our Benediction therapists are equipped as compassionate Grief Companions and we would be honored to journey with you in your grief.
Have you have lost a significant person (or pet or relationship or opportunity) in your life? These significant losses can be terribly painful and disorienting. You know there is an emotional process to help you recover from that loss. This process can feel elusive, consuming or anything in-between! We have heard about grief before, and may even be familiar with the common emotions involved in grieving. But what are we actually doing when we grieve? Let’s clear up this grief thing!
Bereavement and Mourning and Grief are all words related to processing a significant loss. Bereavement is what happens to us—we lost someone important. Bereavement literally means “to be torn apart” and “to have special needs.” Aren’t those statements relatable? Grief is what we think and feel internally after a significant loss. This is a very natural process of integrating the loss and learning to move forward after the loss. Mourning is what we can do to externalize what we are thinking and feeling. Mourning is how we heal in our grief. The grief process is so unique to each person and to each specific loss. Each of us manage our emotions differently. Some internalize emotion and others externalize emotion. Regardless of what we are feeling, different personalities land on different emotions more regularly—emotions like shame, anger or fear. We all have a different relationship with sadness, depending on our exposure to sadness and how sadness was modeled for us throughout our life. The emotions we feel about a particular loss are completely intertwined with the emotions we hold about the relationship with that person. If there was deep love and respect in our relationship with the person lost, then these feelings are going to be very present in the grief process. If there was tension or hurt or unspoken conversations, then those complicated feelings are going to be very present through the grieving process. Now that we know we need to externalize our grief emotions through the process of mourning in order to heal, what does that even look like? This can take the form of journaling, artwork, listening to music or finding movement to express those internal thoughts and emotions. Mourning can be embraced and enhanced through conversations with caring people. Sharing about our loved one can be the most beneficial way to externalize our grief feelings, remembering our loved one and integrating their loss. We like to call this grief companioning. Each of our therapists are trained in this special way of being with those who are grieving, to soften their healing journey and to honor the person they have lost. Social anxiety can be consuming and can really limit the life experiences one might be open to. Imagine having to overcome a wave of panic, accompanied with rapid heartbeat, muscle tension and even blurry vision when walking into certain social circumstances. This dizzying experience can feel disorienting and even dissociative. When this happens regularly, it is understandable that we might start to avoid situations that cause this response all together. When this becomes a pattern, we may experience a narrowing of life experiences, a decrease in self-esteem and a reduced willingness to try new things.
It is possible to learn skills that help us navigate social events with more ease. Feeling confident and calm in social situations allow us to be present with ourselves and with others in the room. We are more able to be genuine and operate within our natural personality, making higher quality connections. There is one skill that has been the most helpful for our clients who are unlearning social anxiety. It is the DBT Mindfulness skill OBSERVATION. To understand this skill the most, let’s take a quick look at Mindfulness. When we are practicing mindfulness, we are 1) noticing our internal/external environment,2) without judgement and 3) without minimizing or enhancing what we find there. It is simply a practice of noticing. Noticing what we are feeling in any given moment. Noticing what is happening around us. Noticing what might feel like a threat. Simply noticing. Mindfulness practices like this slow us down and bring us into the present moment. And when we break this mindful practice into even smaller skills, one of the most impactful skills is that of OBSERVATION. We are simply taking in information, through our senses, thought processes and relationships. To observe skillfully, we need to create enough distance from what we are encountering to fully take it in. And this observable distance can make a big difference for social anxiety. Let me explain a little more clearly. Imagine yourself preparing to go to a social event where you do not know anyone. You are expecting to walk into a room of people milling around and forming small conversation groups, and you are expected to go and have a good time. Practically speaking, this might be a business networking event, an awards ceremony, a college orientation day, etc. What I am encouraging you to try, is to enter the event as an OBSERVER first and foremost. Find a comfortable place in the room to sit or stand. Once you are there, take a few deep breaths that bring you into the present moment and allow the room to stop spinning. As you do this, you are creating an observable distance from which you can take in all that is happening in the room in that moment. Notice what is happening around you. Notice how many conversation groupings there are, how are the people in conversation feeling, are there other nervous people present, where are the food and beverages located, are there people who are also looking for someone to talk with? You are simply noticing what is happening in the room. And from this observation point, you might start to notice where you’d like to be in the room. You may prefer to stay right where you are at, you may notice a conversation you’d like to join, you may notice that you’d like to get a drink before doing anything else. Regardless of where you go from here, mindfully observing your surroundings has allowed you more choice to be genuine in your interactions. And with practice, you may just feel more open and confident in new social situations! |
Archives
April 2024
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed