|
In the journey of healing from trauma, fostering self-compassion is not only crucial but also deeply transformative. Here, we delve into practical steps individuals can take to cultivate self-compassion as they navigate the complexities of trauma recovery.
1. Mindfulness Practices: Begin by cultivating awareness of your thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations without judgment. Mindfulness allows you to observe your inner experience with curiosity and kindness, rather than getting caught up in self-criticism or rumination. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, body scans, and mindful breathing can help anchor you in the present moment and cultivate a compassionate attitude toward yourself. 2. Self-Kindness vs. Self-Criticism: Notice the ways in which you speak to yourself and challenge the inner critic with self-kindness. When faced with self-critical thoughts, imagine what you would say to a close friend experiencing similar struggles. Offer yourself words of encouragement, validation, and support, acknowledging that you are doing the best you can in challenging circumstances. 3. Self-Compassionate Self-Talk: Develop a repertoire of compassionate phrases or mantras to soothe and reassure yourself in times of distress. Repeat these phrases regularly, especially when facing triggers or difficult emotions. Examples include, "May I be kind to myself in this moment," "I am worthy of love and understanding," and "I am not alone in my struggles." 4. Cultivate a Supportive Inner Dialogue: Engage in a compassionate inner dialogue, acknowledging your experiences with empathy and understanding. Reflect on the ways in which you have shown resilience and strength in the face of adversity. Celebrate your progress, no matter how small, and recognize that healing is a journey that unfolds gradually over time. 5. Practice Self-Care: Prioritize activities and practices that nourish your body, mind, and spirit. Engage in activities that bring you joy, relaxation, and a sense of fulfillment. Whether it's spending time in nature, practicing yoga, or connecting with loved ones, self-care is an essential aspect of self-compassion and healing. 6. Seek Support: Reach out for support from trusted friends, family members, or mental health professionals who can offer validation, empathy, and guidance on your healing journey. Surround yourself with individuals who uplift and support you, and don't hesitate to ask for help when needed. By incorporating these practices into your daily life, you can cultivate a compassionate relationship with yourself that serves as a cornerstone of your healing journey. Remember, self-compassion is not about denying your pain or minimizing your experiences but rather embracing yourself with kindness, understanding, and acceptance as you navigate the path toward healing and wholeness.
0 Comments
In the wake of trauma, amidst the pain and challenges, there exists a profound opportunity for growth and resilience known as post-traumatic growth (PTG). This transformative process involves finding meaning, cultivating resilience, and experiencing personal growth in the aftermath of adversity. When healing from trauma, it is essential to understand PTG and how it intertwines with the healing of the nervous system.
Post-traumatic growth is not about minimizing the impact of trauma or dismissing the pain it causes. Instead, it acknowledges that trauma can catalyze profound inner change and transformation. Through PTG, individuals may develop a deeper appreciation for life, experience increased personal strength, forge deeper connections with others, and discover new possibilities for growth and fulfillment. Central to the process of post-traumatic growth is the healing of the nervous system. Trauma can dysregulate the autonomic nervous system, leaving individuals in a state of chronic stress, hypervigilance, or dissociation. However, through interventions such as trauma-informed therapy, mindfulness practices, and somatic experiencing, it's possible to restore balance and resilience to the nervous system. These approaches help individuals regulate their stress responses, release stored trauma from the body, and cultivate a greater sense of safety and well-being. Fostering post-traumatic growth requires a safe and supportive therapeutic environment where individuals feel empowered to explore their experiences and emotions. By validating their struggles and offering tools for healing, therapists can guide clients on a journey of self-discovery and transformation. Through compassionate listening, empathy, and unconditional positive regard, therapists can help individuals navigate the complexities of trauma and embrace the potential for growth and resilience. While the path to post-traumatic growth may be challenging, it offers hope and possibility for those who have experienced trauma. By embracing the journey of healing, individuals can cultivate resilience, find meaning in their experiences, and ultimately thrive in the face of adversity. For us therapists, it is a privilege to witness the resilience and strength of individuals as they embark on this transformative journey toward post-traumatic growth. In conclusion, post-traumatic growth is a testament to the human spirit's capacity for resilience and transformation. By understanding the role of the nervous system in trauma healing and creating a supportive therapeutic environment, trauma specialists can facilitate this process of growth and empowerment. Together, we can honor the courage and resilience of trauma survivors as they navigate the path toward healing, growth, and a renewed sense of purpose. When discussing Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) with clients in the aftermath of their traumatic experience, we have noticed a recurring experience. Many times, clients who meet criteria for the diagnosis of PTSD understand this to mean that they will always suffer from the effects of their trauma. All too often, we see a shadow sweep over our client’s faces as shame and fear rise in their bodies. We want to help clarify this particular diagnosis with a message of hope. PTSD is not a lifelong chronic condition, rather a description of how our bodies work to restore safety after trauma. Let’s talk about Post Traumatic Stress and how we can use this information to work toward healing.
Post-traumatic stress (PTS) is a natural response to experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, impacting both mind and body. When confronted with trauma, the body's nervous system initiates a complex cascade of responses aimed at survival. Understanding the neurobiological impact of trauma can shed light on the symptoms individuals may experience, such as hypervigilance, flashbacks, and emotional dysregulation. Understanding PTS must involve the nervous system's role in trauma, which illuminates how our body reacts to perceived threats. Traumatic experiences can dysregulate the autonomic nervous system, leading to a state of hyperarousal or dissociation. This dysregulation can disrupt the body's ability to distinguish between real and perceived danger, resulting in ongoing feelings of fear and vulnerability. By learning about the nervous system processes at play, individuals can gain insight into their symptoms and recognize that they are not signs of weakness but rather adaptive responses to overwhelming circumstances. This knowledge can also inform treatment approaches, emphasizing interventions aimed at regulating the nervous system's stress response. Treatment for PTS often involves therapeutic modalities that target both the mind and body. Polyvagal theory helps to pay attention to nervous system signals and to use this information to create safety in the mind and body. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) helps individuals become skillful in mindfulness, emotional regulation, interpersonal skills and distress tolerance, while somatic experiencing focuses on releasing stored trauma from the body. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and Brainspotting harness the brain's natural healing mechanisms to reprocess traumatic memories and alleviate distress. These approaches not only address psychological symptoms but also aim to restore balance to the nervous system. Despite the challenges posed by PTS, there is hope for recovery. With the right support and resources, individuals can learn to regulate their nervous system responses, reduce symptoms, establish safety and cultivate resilience. It's essential to approach treatment with compassion and patience, recognizing that healing is a gradual process that unfolds over time. In conclusion, understanding the neurobiological impact of trauma is crucial for navigating post-traumatic stress with compassion and efficacy. By integrating this knowledge into psychoeducation and treatment approaches, we can empower individuals to reclaim agency over their healing journey. Remember, recovery is possible, and there is hope for a brighter future beyond trauma's shadow. Next week’s blog post will be about Post Traumatic Growth. In the ups and downs of our lived experience, our nervous system translates and stores the impact of what we experience. Trauma disrupts the delicate balance of our nervous system, leaving behind discordant echoes that reverberate through our bodies, minds, and spirits. Today, we explore a healing journey informed by Polyvagal Theory, illuminating the pathways to safety and healing after trauma.
The Polyvagal Perspective on Trauma Polyvagal Theory, pioneered by Dr. Stephen Porges, offers a revolutionary lens through which to understand the impact of trauma on the nervous system. At its core lies the recognition that our autonomic nervous system – comprised of the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches – plays a pivotal role in regulating our responses to threat and safety. Trauma hijacks the autonomic nervous system, propelling us into states of hyperarousal or hypoarousal. Hyperarousal, characterized by the activation of the sympathetic "fight or flight" response, plunges us into a state of vigilance and reactivity. Conversely, hypoarousal triggers the parasympathetic "freeze" response, leading to dissociation and disconnection from our internal landscape. The Quest for Nervous System Safety In the aftermath of trauma, reestablishing physical, emotional and relational safety becomes top priority– not just as a concept but as a physiological imperative. Nervous system safety transcends mere physical refuge; it encompasses the restoration of neurophysiological equilibrium, allowing us to navigate the world with a sense of calm and connection. Central to Polyvagal Theory is the concept of ventral vagal engagement – a state of social engagement and connection fostered by the parasympathetic nervous system. Cultivating ventral vagal pathways is essential for re-establishing safety after trauma, facilitating intimacy, trust, and attunement in our relationships. In the realm of Polyvagal Theory, healing unfolds within the crucible of safe and supportive relationships. Co-regulation – the reciprocal exchange of physiological and emotional cues – serves as the cornerstone of healing, offering a roadmap for navigating the complexities of interpersonal connection with grace and compassion. Embodied Resilience and Empowerment Resilience, from a Polyvagal perspective, is not merely a psychological construct; it's an embodied state of being. Embodied resilience entails attuning to the wisdom of our bodies, harnessing the innate capacity for self-regulation, and integrating our experiences into the tapestry of our being with gentleness and acceptance. Empowerment begins with understanding. Polyvagal literacy equips us with the knowledge and insight to navigate the terrain of trauma with clarity and agency. It invites us to become fluent in the language of our nervous system, attuning to its cues and messages with curiosity and compassion. Nurturing Hope Through Nervous System Awareness In the vast expanse of trauma's aftermath, hope emerges as a guiding light – a beacon of possibility beckoning us towards healing and wholeness. Polyvagal awareness infuses hope with substance, grounding it in the neurophysiological realities of our embodied experience and illuminating the path towards transformation. In closing, the journey of healing after trauma, as illuminated by Polyvagal Theory, is a testament to the resilience of the human spirit and the transformative power of connection. May we remember that healing is not just a destination but a sacred unfolding – a journey of rediscovery, reclamation, and profound self-compassion. So, to all those embarking on this nervous system healing path, know that you are not alone. Within the wisdom of your nervous system lies the map to healing and wholeness. And as you navigate the terrain of trauma with courage and grace, may you find solace in the knowledge that safety, connection, and resilience are not just within reach – they are your birthright. Embrace the journey, dear reader, for within its twists and turns lies the promise of a life reclaimed, a spirit renewed, and a heart restored to its truest rhythm. And it is our privilege to provide guidance, safety and relational support on the path of healing and restoration. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) offers a set of skills to help with many different emotional and relational difficulties. The four pillars of DBT are Mindfulness, Emotion Regulation, Interpersonal Effectiveness and Distress Tolerance. Each of these pillars offers a number of skills to practice in that area. I have selected three DBT skills that I believe can make a significant difference for those managing depression.
Depression is an experience that includes a slow-down or freeze response in the nervous system. People managing depression may feel numb, detached, hopeless and sad. These internal experiences may cause them to isolate from relationships, get stuck in their difficult emotions, struggle to complete normal activities. Often, those managing depression feel misunderstood by the people in their life, especially when they are encouraged to “think positively” and “just get over it.” In fact, people managing depression are often expending enormous effort to engage in their life in the most simple ways. The following set of DBT skills can be used together or individually to improve depression symptoms and help catalyze healing and forward movement. 1.Emotion Regulation Skill: Opposite Action When we are using Emotional Regulation skills, we are paying attention to whether or not our emotions fit the situation we are in. Opposite Action is a skill that we reach for when we have determined that our emotions DO NOT fit the facts of the situation. This is often the case with depression. Depression is like a lens that makes life look harder and sadder than it actually is. All emotions have an action urge, an instinctual action that the emotion makes us want to do. When our emotions DO NOT fit the situation, we benefit from acting opposite to the action urge. Here are some common emotions experienced in depression and suggestions for opposite action.
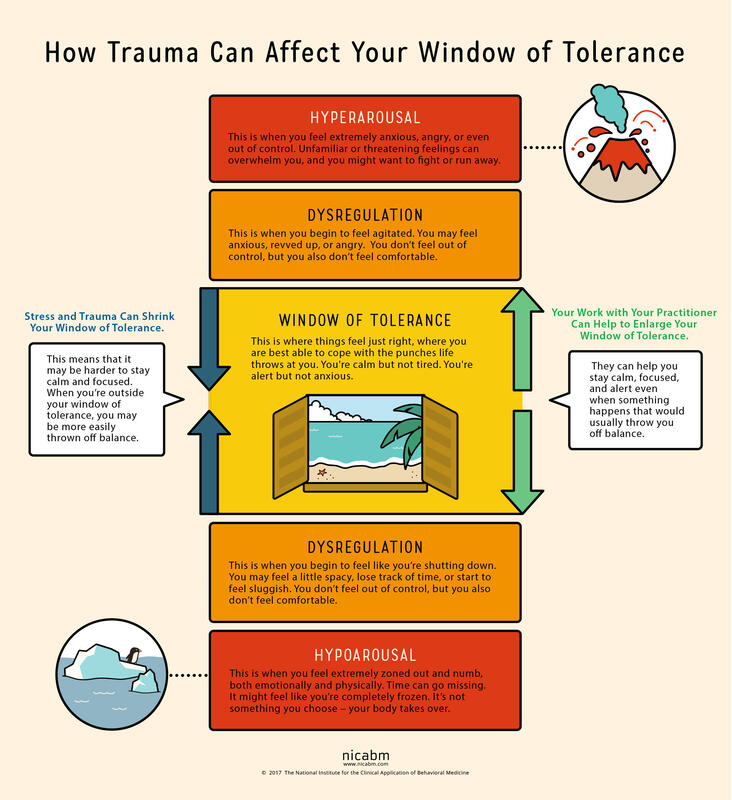
2.Interpersonal Effectiveness Skill: Making Requests Making Requests is a relationship skill that is very closely related to making boundaries. Requests highlight what we need from another person. While they can be vulnerable to make, they are also vital to communicating our needs with others. Loved ones are not mind-readers and need invitations and instructions to know how to care for those managing depression. People experiencing depression are almost always misunderstood by the people who care for them most. Unless they have experienced depression themselves, loved ones will likely minimize the depressed experience. From the outside, it may appear that it would only take a few simple steps to recover from depression. If only that were true. In order to stay connected with loved ones and to receive the care they absolutely need, those managing depression need to lean into this skill of making requests. They need to speak about how they are feeling and the effort they are expending to engage with their lives. They need to ask their loved ones to be patient with them, to use encouraging language, to offer comfort and presence rather than solutions. 3.Distress Tolerance Skill: Radical Acceptance We reach for distress tolerance skills when we are going through circumstances that are too big and/or too hard for us to change. Depression often comes on the tails of a big and hard life event, such as the loss of a loved one, a difficult transition, a painful event or unmovable circumstances. When there is truly nothing we can do to change our circumstances, we need to shift our focus toward acceptance. We are using radical acceptance skills when we work to create openness and willingness toward our difficult circumstances. Willingness is a powerful mindset shift and means that we will stop fighting against what is inevitable. Endlessly fighting against unfavorable circumstances is a recipe for suffering. Pain is inevitable in our lives, but suffering is a choice. We can still live meaningful lives in the midst of painful circumstances. When we give up the fight, we are more able to find acceptance. . . and peace. Living with depression can be a completely consuming experience. Those experiencing depression can have symptoms like persistent sadness, hopelessness, lethargy, low self-esteem, guilt, worthlessness, and more. These symptoms exist on a spectrum from mild to severe and short to long-term. Living day to day with depression feels heavy, aimless and dark. Often people suffering from depression are told to change their mindset in order to recover. We know that change must come from a much deeper place. In fact, living day to day with depression requires enormous amounts of courage and perseverance, and it helps those who are suffering to have this acknowledged and validated. Depression has several different causes and sources. There are strong inherited patterns for major depression. There are also significant hormonal impacts, especially in post-partum depression and pre-menstrual depressive disorder. Personality also has a strong influence on mood and energy and motivation. All of these different also create causes can also produce a predisposed sensitivity to depression. This blog post is to highlight when life circumstances or traumas are the source of depression. When this is the case, it is the nervous system that is leading the body and mind toward depression. And as such, treatment will need to be focused on healing the nervous system and helping the client work toward a different nervous system state. When the nervous system (read: trauma, overwhelm, life circumstances) is causing depression, healing must happen deeply in the autonomic (involuntary) nervous system. To understand the nervous system impact and the healing of nerves, we need to understand the Window of Tolerance. When we are in the window of tolerance, we are grounded, flexible and able to roll with the ups and downs of life. When we have a good amount of resilience, our window of tolerance is large and we are able to handle significant challenges without becoming too dysregulated. When we are under a lot of stress, our window of tolerance shrinks and we start to experience hyper or hypo arousal. Let’s discuss these nervous system states that exist outside of the window of tolerance. When we experience overwhelming stressors, we become dysregulated in one of two different directions, sometimes cycling between the two. We can become activated and have a flood of anxious or angry energy wash through our body (hyperaroused). Or we can become deactivated and experience numbness and a shut down response (hypoarousal). This hypoaroused state is the embodiment of depression. This is how stressors or traumas cause depression.
Hypoarousal symptoms also exist on a spectrum. On the milder side, we might experience tiredness, brain fog and a slump in energy. When hypoarousal is heightened, one might experience emotional numbness, dissociation, and even catatonia. Sometimes, we end up in this depressed state after an extended period of stress. It’s like our system is saying that it can’t handle that level of activation for that long and it shuts down. In other words, depression can be caused by a nervous system shut down. So, what does our nervous system need when it is in this shut down state? Sometimes, it simply needs a break. It needs rest from the hyper-activated state. The nerve that runs these activation pathways has become raw and overworked and needs to be soothed. The nervous system also has a significant need for connection when it is in this state of shut down. It needs a form of connection that is accepting, supportive and understanding. The nervous system also needs a way to process or integrate the overwhelming emotions that shut it down in the first place. This typically needs to happen at a slow and measured pace, so not to overwhelm again. These interventions serve as a ladder that helps us climb out of the shut down state, closer and closer to that window of tolerance. For a sustained healing process, we also need to take a good look at our lifestyle. When healing from a nervous system shut down, we need to choose a gentle pace of life, avoiding any additional stressors when possible. We can boost our nervous system health with meditation and mindfulness skills. We can invest in sustainable sleep habits that allow our entire system to regenerate every night. Gentle, joyful movement practices can also lift us out of shut down or depression. We at Benediction honor your nervous system and it’s inherent needs and functions, and we know how to move you out of harmful nervous system pathways. We can help you reconnect with yourself and with others by bringing your system back into balance in that lovely window of tolerance. |
Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed